What Are Causes of Brain Stroke & Its Treatment
Summary: Stroke, also called cerebrovascular accident or brain attack, is a sudden impairment of cerebral circulation in one or more of the blood vessels supplying the brain. Strokes interrupt the oxygen supply to the brain tissues and can cause serious damage.
For
anyone who has suffered a stroke, it is vitally important to restore normal
circulation as soon as possible to limit damage to the brain tissues. The
number still hovers around the 30% and stroke could soon be the most common
cause of death worldwide. Of those who do survive, about half remain
permanently disabled and many experience a recurrence within weeks, months or
years.
Causes and Incidence
A
stroke results from obstruction of a blood vessel, typically outside the brain,
but occasionally within the brain itself. Factors that increase the risk of
stroke include a history of transient ischemic attacks, atherosclerosis,
hypertension, kidney disease, arrhythmias (particularly atrial fibrillation),
rheumatic heart disease, diabetes, postural hypertension, heart enlargement,
high serum cholesterol, smoking, lack of exercise, long time use of
contraceptives, obesity and a family history of strokes. Females have
additional risk factors for stroke such as oral contraceptives that are not
present in men. Cocaine induced ischemic stroke is now being reported in
younger patients.
Men
traditionally have had a greater risk of stroke than women but women start
catching up to men five or 10 years after menopause. While stroke is most
common in the elderly, people of any age and any level of physical fitness can
suffer the injury. A persons risk of dying if he or she does have a stroke also
increases with age.
Stroke
is uncommon in children accounting for only a small percentage of stroke cases
each year. Stroke in children is often secondary to congenital heart disease,
abnormalities of intracranial vessels genetic disorders and blood disorders
such as thrombophilia.
Types of Stroke
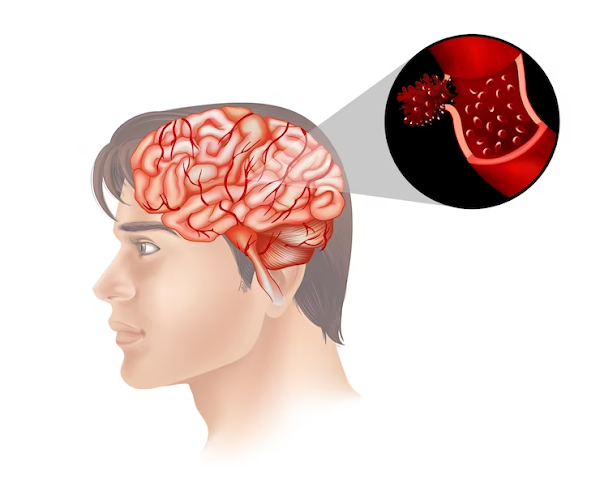
Strokes can be classified into two major categories: ischemic and hemorrhagic, 80% of strokes are due to ischemia, the rest are due to hemorrhage.
The major causes of stroke
are thrombosis, embolism and hemorrhage:
· Donate to veterans with a brain injury is the most common cause in middle age and elderly people as they tend to have a higher incidence of arterial plague, diabetes or hypertension. It can occur at any age, especially in those with a history of rheumatic heart disease, endocarditis, cardiac arrhythmias, or after open heart surgery.
·
Embolism is the second
most common cause of stroke. Embolisms occur when a blood vessel is blocked by
a clot, a tumour, fat, bacteria or air. Embolisms usually develop within 10 to
20 seconds and without warning and when they reach the brain, will cut off
circulation by lodging in a narrow part of an artery causing swelling and
tissue death.
· Hemorrhage the third most common type of stroke, which is more prevalent in women than men, like embolism can occur suddenly at any age. It results from chronic hypertension or from aneurysms that cause a sudden rupture of a cerebral artery.
For
people referred to the emergency room, early recognition of stroke is deemed
important as this can expedite diagnostic tests and treatments. Strokes due to
thrombosis embolism, or arterial spasm, which cause ischemia, must be
distinguished from those due to hemorrhage, which are usually severe and often
fatal. Stroke is diagnosed through several techniques: observation of clinical
features, a neurological examination, CT scans or MRI scans, Doppler
ultrasound, and arteriography. Stroke support group help to live a healthy life.
Treatment
Surgery
to improve cerebral circulation, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) for clot
dissolution, anti-coagulants and anticonvulsants are commonly used to treat
stroke. Treatment to break up a blood clot, the major cause of stroke, must
begin within three hours of the stroke to be effective. The treatment must be
administered within three hours of the stroke event. Therefore, patients who
awaken with stroke symptoms are ineligible for the therapy, as the time of
onset cannot be accurately determined. Patients with clot-related (thrombotic
or embolic) stroke who are ineligible for treatment may be treated with heparin
or other blood thinners, or with aspirin or other anti-clotting agents in some
cases.
Prevention
Generally
there are three treatment stages for stroke: prevention, therapy immediately
after the stroke, and post stroke rehabilitation. Therapies to prevent a first
or recurrent stroke are based on treating an individual’s underlying risk
factors for stroke, such as hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and diabetes.
Lowering blood pressure has been conclusively shown to prevent both ischemic
and hemorrhagic strokes. Aspirin prevents against first stroke in patients who
have suffered a myocardial infarction. Nutrition, specifically the
Mediterranean-style diet, has the potential of more than halving stroke risk.
Rehabilitation
Stroke
may cause problems with thinking, awareness, attention, learning, judgment, and
memory. Survivors often have problems understanding or forming speech, they may
have difficulty controlling their emotions or may express inappropriate
emotions. They may also have numbness or strange sensations.

Comments
Post a Comment